Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Matsuda, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Maekawa, Fujio
EPJ Web of Conferences, 239, p.06004_1 - 06004_4, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:72.11(Nuclear Science & Technology)For the Accelerator-Driven nuclear transmutation System (ADS), nuclide production yield estimation in the lead-bismuth target is important to manage the target. However, experimental data of nuclide production yield by spallation and high-energy fission reactions are scarce. In order to obtain the experimental data, we experimented in J-PARC using  Pb and
Pb and 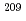 Bi samples. The samples were irradiated with protons at various kinematic energy points between 0.4 and 3.0 GeV. After the irradiation, the nuclide production cross section over
Bi samples. The samples were irradiated with protons at various kinematic energy points between 0.4 and 3.0 GeV. After the irradiation, the nuclide production cross section over  Be to
Be to 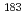 Re was obtained by spectroscopic measurement of decay gamma-rays from the samples with HPGe detectors. The present experimental results were compared with the evaluated data (JENDL-HE/2007) and the calculation with the PHITS code and the INCL++ code. The present experiment data showed consistency with other experimental data with better accuracy than other ones. In reactions to produce light nuclides, JENDL and calculation with the PHITS and INCL++ for
Re was obtained by spectroscopic measurement of decay gamma-rays from the samples with HPGe detectors. The present experimental results were compared with the evaluated data (JENDL-HE/2007) and the calculation with the PHITS code and the INCL++ code. The present experiment data showed consistency with other experimental data with better accuracy than other ones. In reactions to produce light nuclides, JENDL and calculation with the PHITS and INCL++ for  Be production agreed with the data.
Be production agreed with the data.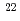 Na production, however, underestimated about 1/10 times. For middle to heavy nuclide productions cases, both calculations agreed with the experiment by a factor of two. JENDL showed lower energy having a maximum value of excitation function maximal value than the experimental data.
Na production, however, underestimated about 1/10 times. For middle to heavy nuclide productions cases, both calculations agreed with the experiment by a factor of two. JENDL showed lower energy having a maximum value of excitation function maximal value than the experimental data.
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(3), p.276 - 290, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:23.63(Nuclear Science & Technology)This paper presents an approach to uncertainty estimation of spallation particle multiplicity of lead ( Pb), primarily focusing on proton-induced spallation neutron multiplicity (
Pb), primarily focusing on proton-induced spallation neutron multiplicity (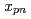 ) and its propagation to a neutron energy spectrum. The
) and its propagation to a neutron energy spectrum. The 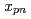 uncertainty is estimated from experimental proton-induced neutron-production double-differential cross sections (DDXs) and model calculations with the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS). Uncertainties in multiplicities for
uncertainty is estimated from experimental proton-induced neutron-production double-differential cross sections (DDXs) and model calculations with the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS). Uncertainties in multiplicities for 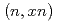 ,
, 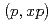 , and
, and 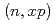 reactions are then inferred from the estimated
reactions are then inferred from the estimated 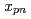 uncertainty and the PHITS calculation. Using these uncertainties, uncertainty in a neutron energy spectrum produced from a thick
uncertainty and the PHITS calculation. Using these uncertainties, uncertainty in a neutron energy spectrum produced from a thick  Pb target bombarded with 500 MeV proton beams, measured in a previous experiment, is quantified by a random sampling technique, and propagation to the neutron energy spectrum is examined. Relatively large uncertainty intervals (UIs) were observed outside the lower limit of the measurement range, which is prominent in the backward directions. Our findings suggest that a reliable assessment of spallation neutron energy spectra requires systematic DDX experiments for detector angles and incident energies below 100 MeV as well as neutron energy spectrum measurements at lower energies below
Pb target bombarded with 500 MeV proton beams, measured in a previous experiment, is quantified by a random sampling technique, and propagation to the neutron energy spectrum is examined. Relatively large uncertainty intervals (UIs) were observed outside the lower limit of the measurement range, which is prominent in the backward directions. Our findings suggest that a reliable assessment of spallation neutron energy spectra requires systematic DDX experiments for detector angles and incident energies below 100 MeV as well as neutron energy spectrum measurements at lower energies below  1.4 MeV with an accuracy below the quantified UIs.
1.4 MeV with an accuracy below the quantified UIs.
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(2), p.160 - 171, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:31.36(Nuclear Science & Technology)We present a new model to describe the fission probability of the high-energy fission model, as deduced from the intranuclear cascade calculation with the Intra-Nuclear Cascade model of Li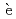 ge (INCL) version 4.6 and Prokofiev's phenomenological systematics of the proton-induced fission cross sections. This model is implemented in the de-excitation model of the Generalized Evaporation Model (GEM), and applied to Monte Carlo spallation reaction simulation using the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS). Comparing with experimental data for subactinide nuclei shows that this model can provide a unified prediction of the proton-, neutron-, and deuteron-induced fission cross sections with markedly improved accuracy. The calculated fission fragments tend to shift to higher mass numbers. To account for the isotopic distributions of fission fragments within the framework of a coupled INCL/GEM, modification of INCL is required, especially for description of the highly-excited states of residual nuclei.
ge (INCL) version 4.6 and Prokofiev's phenomenological systematics of the proton-induced fission cross sections. This model is implemented in the de-excitation model of the Generalized Evaporation Model (GEM), and applied to Monte Carlo spallation reaction simulation using the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS). Comparing with experimental data for subactinide nuclei shows that this model can provide a unified prediction of the proton-, neutron-, and deuteron-induced fission cross sections with markedly improved accuracy. The calculated fission fragments tend to shift to higher mass numbers. To account for the isotopic distributions of fission fragments within the framework of a coupled INCL/GEM, modification of INCL is required, especially for description of the highly-excited states of residual nuclei.
Matsuda, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Iwamoto, Hiroki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(8), p.955 - 961, 2018/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:45.59(Nuclear Science & Technology)We have started an experimental program to measure activation cross sections systematically in the proton-induced spallation reaction in structural materials commonly used in high-intensity proton accelerator-based facilities, such as Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC). As the first step of the program, aluminum (Al) was chosen to verify the adequacy of the measurement technique implemented in a J-PARC proton beam environment because data of Al have been relatively well studied both by experimental measurement and simulation. Activation cross sections of  Be,
Be,  Na, and
Na, and  Na in Al were measured at proton energy points from 0.4, 1.3, 2.2 to 3.0 GeV, which could be delivered smoothly from the synchrotron. The validity of experimental data has been verified by introducing an effective proton numbers determination procedure. We compared the measured data with existing experimental data, the evaluated data (JENDL-HE/2007), and the calculations with several intra-nuclear cascade models by the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) code. Although the experimental data agreed with JENDL-HE/2007, the calculations underestimated about 40%. This could come from the evaporation model (generalized evaporation model) being implemented in the PHITS code. We found that the calculations agreed with the experimental data by an upgraded PHITS code.
Na in Al were measured at proton energy points from 0.4, 1.3, 2.2 to 3.0 GeV, which could be delivered smoothly from the synchrotron. The validity of experimental data has been verified by introducing an effective proton numbers determination procedure. We compared the measured data with existing experimental data, the evaluated data (JENDL-HE/2007), and the calculations with several intra-nuclear cascade models by the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) code. Although the experimental data agreed with JENDL-HE/2007, the calculations underestimated about 40%. This could come from the evaporation model (generalized evaporation model) being implemented in the PHITS code. We found that the calculations agreed with the experimental data by an upgraded PHITS code.
 C and
C and  Bi in the 20- to 150-MeV energy range
Bi in the 20- to 150-MeV energy rangeE.Kim*; Nakamura, Takashi*; *; Uwamino, Y.*; *; Imamura, Mineo*; Nakao, Noriaki*; *;
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 129(3), p.209 - 223, 1998/00
Times Cited Count:66 Percentile:97.25(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Y.E.Titarenko*; O.V.Shvedov*; V.F.Batyaev*; E.I.Karpikhin*; V.M.Zhivun*; A.B.Koldobsky*; M.M.Igumnov*; I.S.Sklokin*; R.D.Mulambetov*; A.N.Sosnin*; et al.
Proc. of 2nd Int. Topical Meeting on Nuclear Applications of Accelerator Technology (AccApp'98), p.164 - 171, 1998/00
no abstracts in English